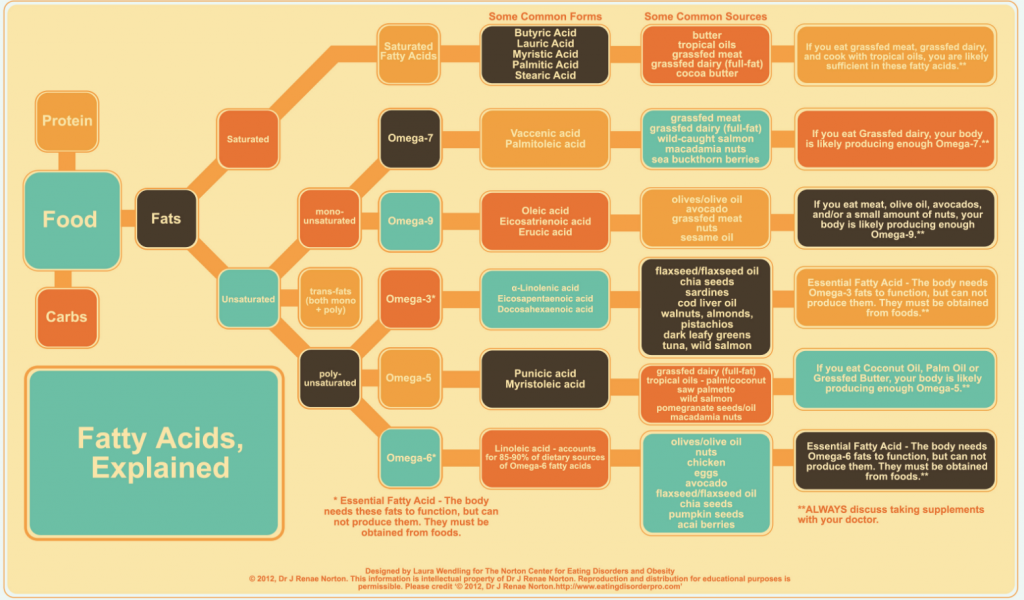
What is a fatty acid?
First up, let’s explain what we mean by fatty acids. These are the building blocks of the fats that we eat.
Essential fatty acids (EFA) are those fats that our body cannot produce and which are essential for our health. Therefore we need to consume them in our diet. There are 2 ‘parent’ categories of EFA’s:
- Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA): Broken down to the active form of EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) these are also called Omega-3 fats
- Linoleic Acid(LA): Broken down to the active form of GLA (Gamma Linoleic Acid) and AA (Arachadonic Acid) these are also called Omega-6 fats
Health benefits of essential fatty acids
We can eat EPA and DHA directly but these food sources are not usually vegan (think oily fish and eggs). The other option is your body converting ALA/LA to EPA/DHA from foods such as nuts and seeds.
As vegans, its really important that we support our body in the conversion of these essential fatty acids. The health benefits are many, but here are the key roles they play in your body
- Reducing joint pain (1)
- Managing and reducing inflammation (2)
- Promoting heart health (3)
- Protecting your brain (4)
- Fighting depression (5)
Deficiencies of EFA’s can lead to symptoms such as:
- Dry, scaly skin
- Dandruff
- Brittle fingernails
- Dry mouth
- Dull, patchy skin
- Cracked fingertips or heels
- Excessive thirst
Handbrakes to converting EFA’s
A number of factors can stop your body from converting essential fatty acids.

- Vitamin/mineral deficiencies: Magnesium, vitamin C, vitamin B complex, zinc and vitamin A are key nutrients.
- Stress
- High alcohol consumption
- Obesity and diabetes
- High sugar intake
If any of these are an issue for you, you may want to consider how you can address them.
Hacks to increase conversion of EFA’s
Add turmeric to your daily routine. A recent study (6) found that daily supplementation of turmeric can help your body convert ALA to DHA. Look to add around 5g per day. Taking more than this can increase your net carb count (1tsp contains around 1.3g net carbs)
Take a few drops of peppermint oil everyday: It helps to increase fatty acid metabolism
Ensure your nutritional status is optimal. If you haven’t had this confirmed by a blood test, common signs and symptoms of low mineral/vitamin status are as follows:
- Magnesium: You may experience muscle cramps, spasms and restless legs. Eye twitches or headaches. You may have low energy and find it difficult to fall asleep at night.
- Vitamin C: Bleeding gums, re-current infections and slow wound healing.
- Zinc: Brittle hair, nails and dry skin. Re-current infections and slow wound healing may indicate low zinc status.
- Vitamin B complex: Numbness, tingling and strange sensations in the body. Low energy and poor sleep quality. More difficulty than normal in coping with stressful periods in life.
- Vitamin A: Dry eyes and skin. Difficulty seeing in low light and re-current infections.
This list is just a general guide. However, if you do suspect you are deficient, it would be worthwhile talking to your healthcare provider.
Limiting sugar and alcohol is a given on the ketogenic diet, so you’re already on your way to removing these handbrakes.
Sources:
(1) Geusens, P., Wouters, C., Nijs, J., Jiang, Y. and Dequeker, J. (1994), Long-term effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 37: 824–829. doi:10.1002/art.1780370608
(2) Stefan Endres, M.D., Reza Ghorbani, B.S., Vicki E. Kelley, Ph.D., Kostis Georgilis, M.D., Gerhard Lonnemann, M.D., Jos W. M. van der Meer, M.D., Joseph G. Cannon, Ph.D., Tina S. Rogers, Ph.D., Mark S. Klempner, M.D., Peter C. Weber, M.D., Ernst J. Schaefer, M.D., Sheldon M. Wolff, M.D., and Charles A. Dinarello, M.D. (1989), The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with n—3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Synthesis of Interleukin-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor by Mononuclear Cells. N Engl J Med, 320:265-271. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501
(3) Pan A, Chen M, Chowdhury R, et al. α-Linolenic acid and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2012;96(6):1262-1273. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.044040.
(4) Cole GM, Ma Q-L, Frautschy SA. Omega-3 fatty acids and dementia. Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and essential fatty acids. 2009;81(0):213-221. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2009.05.015.
(5)Grosso G, Pajak A, Marventano S, et al. Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Treatment of Depressive Disorders: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Malaga G, ed. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(5):e96905. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096905.
(6) Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):951-61. Curcumin boosts DHA in the brain: Implications for the prevention of anxiety disorders. Wu A1, Noble EE1, Tyagi E1, Ying Z1, Zhuang Y1, Gomez-Pinilla F2.

